Google Forms is a popular free tool for creating surveys, quizzes, and forms. One powerful feature it offers is conditional questions, also known as conditional logic or branching logic. Conditional questions allow a form to change dynamically based on a respondent’s answers, for example, skipping or adding questions depending on what the user selects.
This makes forms more efficient and personalized because respondents only see questions that are relevant to them. Instead of forcing users to go through every question, conditional logic helps reduce confusion and fatigue, which can significantly improve the overall user experience and increase form completion rates.
In this guide, we’ll explain how to set up conditional questions in Google Forms step by step.
What Are Conditional Questions in Google Forms?
Conditional questions are questions that appear or are skipped based on a respondent’s previous answer. In Google Forms, this feature is implemented using “Go to section based on answer.” Instead of showing or hiding individual questions, Google Forms sends respondents to different sections depending on how they respond to a specific question.
For example, a customer feedback form might ask, “Are you satisfied with our service?” If the respondent selects No, the form can direct them to a section with follow-up questions about what went wrong. If they select Yes, the form can skip those questions and move to a section asking what they liked most. This creates a more tailored experience and leads to more accurate and useful responses.
It’s important to note that Google Forms’ conditional logic works only at the section level. You can’t apply logic to individual questions within the same section. Additionally, conditional branching is limited to multiple-choice and dropdown question types. Other formats, such as short answers, checkboxes, or scales, can’t be used to trigger conditional paths.
Understanding these limitations is important before building your form, especially if you need complex logic or highly personalized user journeys.
How to Set Up Conditional Questions in Google Forms
Setting up conditional logic in Google Forms involves using sections and the “Go to section based on answer” feature. Below is a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Create or Open Your Form
Open Google Forms and either start a new form or open an existing one. Add the question that will control the branching (your “parent question”). Example: a Multiple Choice question like “Will you be attending the event?” with Yes/No options.
Step 2: Add Sections for Each Path
Google Forms branches users by sending them to different sections. Click Add section (the two-rectangle icon) and create a section for each outcome.
Example:
Section: “Event Details (Attending)” (for “Yes”)
Section: “Submit / Thanks” (for “No”)
Step 3: Turn on “Go to Section Based on Answer”
Click the parent question → click the ⋮ (More options) menu → select Go to section based on answer. You’ll now see dropdowns next to each answer choice.
Step 4: Set the Branching Rules
For each answer option, pick where the respondent should go next.
Example:
Yes → “Event Details (Attending)”
No → “Submit form” (or a short “Thanks” section)
Step 5: Check What Happens After Each Section
At the bottom of each section, review “After section…” navigation. Most branches should end with Submit form, unless you want users to return to another section afterward. Make sure every path leads somewhere (no dead ends or loops).
Step 6: Preview and Test
Click Preview (eye icon) and test every option to confirm the form jumps to the right section. Try different answers and make sure users can’t skip anything important by accident.
By following the above steps, you can create basic conditional questionnaires in Google Forms. This feature is especially useful for surveys, quizzes, and application forms where different respondents will have different relevant questions. It keeps forms shorter and more focused, which your audience will appreciate, respondents are less likely to abandon the form if they feel it’s tailored to them and not asking pointless questions. In fact, one analysis found that reducing the number of form fields (for example, from 11 down to 4) more than doubled the form completion rate (a 120% increase in completions).
Pro Tip: You can also create online quizzes using AI quiz generator within seconds.
Drawbacks of Google Forms’ Conditional Logic
Google Forms provides a basic branching logic capability, but it may fall short if you need sophisticated or large-scale form logic. Here are some key drawbacks and limitations of Google Forms’ conditional questions:
Section-Based (Not Question-Level) Logic:
Google Forms doesn’t let you show or hide individual questions based on previous answers within the same section. Instead, you have to split the form into multiple sections and route users between them to achieve conditional behavior. This can become cumbersome when you have many conditional questions. A form with lots of small sections takes more time to design, and it’s easier to lose track of the flow compared to tools that allow question-level logic on a single page.
Limited Question Types for Triggers:
Only Multiple Choice and Dropdown questions can trigger conditional branching in Google Forms. You can’t build conditions based on checkboxes, short answers, dates, scales, or other field types. This limits how flexible your form can be. For example, you can’t display a follow-up question based on a keyword someone types into a short answer field, because Google Forms doesn’t support rules driven by text inputs.
No Multi-Condition or Advanced Logic:
Google Forms doesn’t support combining conditions. Each branching rule is tied to a single question’s answer, which means you can’t create compound rules like: “Show Section C only if Question 1 is X and Question 2 is Y.” There’s no IF/AND/OR logic, and you can’t route people based on combinations of answers across multiple questions. This makes it difficult to build complex surveys or application flows that require layered decision-making.
No Conditional Logic on the Same Page:
Because conditional logic relies on sections, you can’t reveal a follow-up question instantly below the current question on the same page. Any conditional path requires a section break, which means the respondent has to click Next and move to another “page” to see what comes next. That can feel less smooth and more fragmented than form builders that support real-time field reveal within the same screen.
Basic Personalization and Outcomes:
Google Forms branching is mostly simple skip logic. It lacks advanced personalization features like showing different custom messages based on answers, displaying tailored end screens, or dynamically changing outcomes. You also can’t do things like calculations, scoring, answer piping (reusing someone’s input later in the form), or other logic-driven personalization inside a standard Google Form experience. The result is that even with branching, the form still feels fairly static.
Design and Branding Limitations:
While this isn’t purely a logic issue, it often matters in real-world use. Google Forms has limited customization, basic colors, fonts, and header images, and the overall design remains recognizably “Google.” For businesses, marketers, or teams running lead generation campaigns, this can be a drawback. Even if the logic works, the form may look generic or not fully aligned with a brand’s style, which can affect trust and engagement.
Maintaining Complex Branches Is Hard:
When a Google Form has many sections and branching rules, updating it can become difficult. Adding a new question, inserting a section, or rearranging the structure may require you to manually revisit and reconfigure multiple “go to section” settings. There’s also no visual logic map, so you’re forced to manage the structure mentally. As the form grows, the risk of misrouting users (or accidentally skipping key questions) increases. In short, Google Forms wasn’t designed for complex decision trees, so large branching setups can quickly become messy and error-prone.
Involve.me: A Better Alternative for Conditional Logic Forms
If Google Forms feels too limited for your conditional logic needs, involve.me is a more advanced alternative. It’s a modern form, quiz, and survey builder designed to create highly personalized, multi-step forms without coding, making it especially useful for businesses and marketers.
Question-Level Conditional Logic:
Unlike Google Forms, involve.me lets you show or hide individual questions, not just sections. This means follow-up questions can appear instantly on the same page based on previous answers, creating a smoother and more natural user experience.


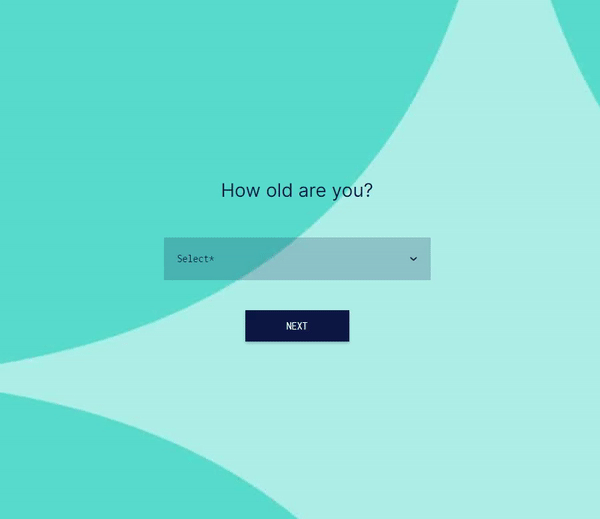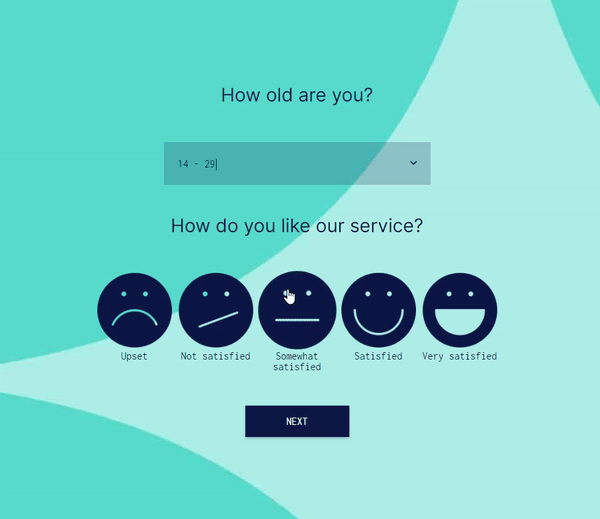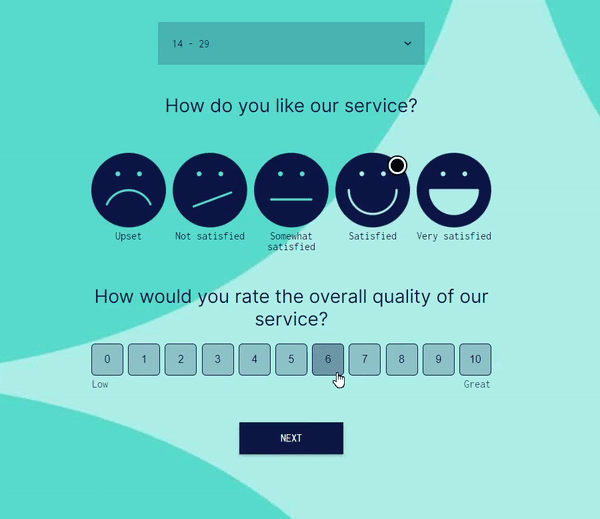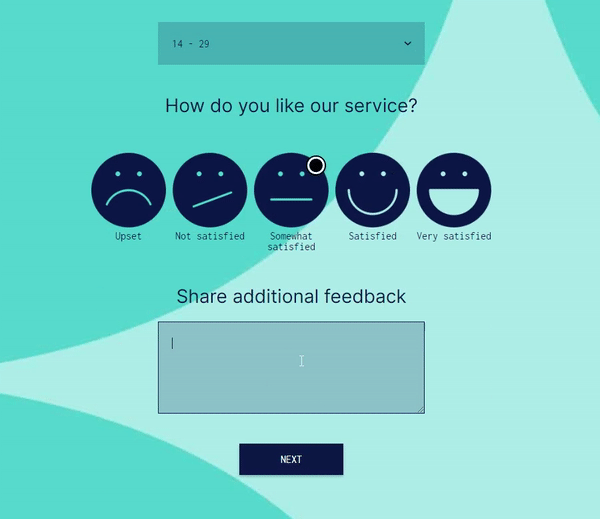
Advanced Logic and Multiple Conditions:
involve.me supports AND/OR logic, multiple conditions, scoring rules, and answer piping. You can build complex decision trees, quizzes, and lead qualification flows that simply aren’t possible with Google Forms’ basic skip logic.
Personalized Outcomes and Thank-You Pages:
You can create different end screens, results pages, or calls to action based on user responses. This makes involve.me ideal for quizzes, lead funnels, and campaigns where personalization directly impacts engagement and conversions.
Better Design and Branding:
With a drag-and-drop editor, involve.me offers full branding control, colors, fonts, layouts, and advanced content elements like images, videos, calculators, and payments. Forms look polished and on-brand rather than generic.
Stronger Integrations and Analytics:
involve.me integrates with CRM, email, and analytics tools, and provides detailed insights such as drop-off rates, completion stats, and segmented responses. This makes it far more suitable for professional and business use cases than Google Forms.
Easy to Use with Built-In Support:
Despite its advanced features, involve.me remains user-friendly with a visual logic builder, ready-made templates, and an AI form builder. Live support and tutorials make it easy to switch from Google Forms and start building more powerful forms right away.
Create Your Own Online Forms
Get Started with 350+ Templates
Contact Form for Real Estate Template
Agency Lead Generation Form Template
Demo Booking Form for Software Template
Final Words
Google Forms is a handy free tool and works for basic conditional questions. If you only need a simple skip logic on a couple of questions, Google Forms can do the job. But if you’re finding its conditional logic too restrictive, or you want to create more engaging, professional forms, then consider switching to a platform like involve.me.
With involve.me, you can build smart forms that truly adapt to each user’s answers, improving user experience and data quality.
Ready to upgrade your forms? Try involve.me for free and explore its conditional logic features firsthand. You can start building an interactive, multi-path form in minutes with its drag-and-drop editor and templates.
Create Your Own Online Forms
involve.me is a powerful no-code solution to build multi-step forms that integrate quiz, survey, and calculator elements







