How can you attract more customers and organic traffic towards your e-commerce store for better sales? The simple answer is SEO.
You need optimization no matter if you’re running a regular blog or a product store.
But, SEO strategies for e-commerce stores are a little different from regular websites.
So, how can you do that? In this post, we look at exactly that.
6 SEO Strategies to Help Boosting Organic Traffic
1. Perform a Technical Audit
There can be many technical issues coming in the way of your eCommerce store gaining good online visibility in search results.
That’s why it pays to run a technical audit which should highlight some of these commonest issues: Here’s a summary of a typical SEO audit -
Check for crawl errors - You can use SEMrush for that. It checks for areas where search engines might be getting stuck while crawling your site.
Perform XML - It helps you check the health of all the pages
Run a mobile-friendly test to see how well the site loads
Review the robots.txt file so that you can check pages that you want to block from search engines and allow any disallowed pages
Check for broken links - You can use Broken Link Checker for that purpose
Check for duplicate content - Use Copyscape for that.
Review H1. H1s tell search engines where the page begins. Look into your crawl report and see if the page has missing H1s or too many of these. Below is a screenshot of how this report might look like in SiteChecker.
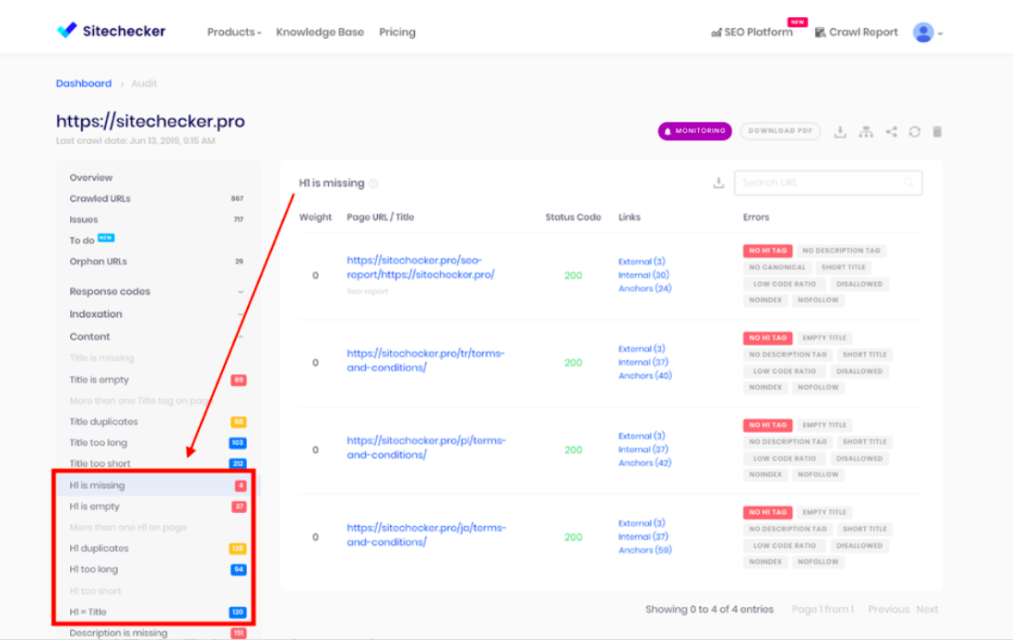
These are only some of the things that a technical SEO audit does. You can go as much into detail as possible.
2. Internal Links
Internal linking can be an excellent and highly under-utilized SEO strategy that can improve your rankings. It’s a great way to set the hierarchy of your pages to tell Google which of the pages are most important on your site.
Try to use relevant anchor texts to see which ones help to improve your rankings for top keywords.

In the above example. ‘Tiny Dancing Horse’ is the example of an ideal anchor text linking the site.
Internal linking is great for cross-selling and upselling products on your website. You can even add them to your post. But, be careful! Do not go overboard with the whole inter-linking of pages and it may make your site look suspicious in the eyes of search engines.
3. Canonical URLs
Some of the longest and messiest URLs belong to eCommerce stores. The problem gets worse as the store gets bigger. And, with the inclusion of navigation systems and search parameters - click paths can build millions of unique URLs.
Many retailers would have a thousand unique variations of a single product. At times this is a necessary evil as you want your customers to find the product they are searching for online.
But, this situation is not ideal for brands and retailers as it can make it difficult for Google to index, crawl, and track down every single version of the same URL.
If you sense that your store also has the same problem, then do use canonical tags to eliminate index bloating. You should also use the parameter exclusion tool by Google to simplify things even further.
Ideally, you should keep the URL clean. Take a look at the example below.
http://example.com/services/index.jsp?category=legal&id=patents
This is an example of a messy/unclean URL as it carries parameters and queries.
Here’s another one instead:
http://example.com/services/legal/patents
The above is what you call a clean URL. Aim for similar URLs.
4. De-index Discontinued Products
It’s common for e-commerce stores to run out of products. There are times when a product is no longer available.
At that time the page may show a 404 error which indicates that the page doesn’t exist any longer. It means that if a browser tries to find any information for that particular page, it won’t find anything.
Unfortunately, these errors can confuse the Google crawlers by trapping them in too many dead ends and redirects.
Therefore, you must have a process in place that automatically keeps removing the product pages that are no longer available or have been discontinued. You can also redirect users to a related family, brand, or category page so they can continue to shop even if the product they’re specifically looking for is no longer available.
Here’s how you can manage product pages that are permanently discontinued.
If you’re sure that the product is permanently discontinued and the page holds no value, you should use your web API to return HTTP status code 410 for that particular page. This will signal Google that the product is no longer available. It will then redirect the visitor to other relevant products.
Doing so will cut down on your crawl budget while also redirecting search engines towards more meaningful parts of the site that need indexing.
5. Clean Up Your HTML
The purpose of HTML or hypertext markup language is to tell the browsers how they should display the content of a site. Search engines also use HTML to understand what the content is all about.
Without HTML users will see nothing but a blank screen or a mess of text. Different elements of HTML such as headers, meta tags, descriptions, title tags, etc. All help to understand what all the page is about.
A few changes here and there could do wonders for your e-commerce store’s SEO.
Define proper class names. Avoid using acronyms while creating IDs and classes. Instead use proper names.
Go for indentation - While indentation will not have any bearing on the page ranking but it does improve the readability.
Minimize the number of ‘divs’. Keep your code clean and delete all of the unnecessary elements.
Keep your CSS and Javascript files external. In this way, you can make all of your future pages use that exact same code without creating a mess or having to redo the whole thing over.
A clean code helps search engines find all the necessary and important information across web pages. A messy HTML might make it difficult for Google to understand the content properly, which inevitably, might affect the SEO.
6. Writing and Content Creation
When it comes to SEO - many people would focus too much on the technical part and not so much on the content portion of the website. But, in the realm of e-commerce stores, do not look only at the structure. You need to focus on content creation and optimization as well.
Here are 10 quick ways you can do it:
Include phrases such as ‘on sale’ and ‘free shipping’ to get maximum CTR.
Aim for at least a thousand words of content and optimize it for keywords repeated 3-5 times all across the content.
Write rich, in-depth product descriptions. It’s only through these descriptions that Google knows and understands where to place a product and make it rank.
Use powerful words that prompt action and drive sales. Aim for compelling product descriptions.
Write as many posts as you can, frequently. Ideally, you should aim for 16 blog posts a month to attract inbound traffic.
Produce content around marketing pieces during peak season as you have a higher likelihood of better conversions at that time.
To rank for organic terms, write longer forms of blog posts.
Whenever possible try to incorporate demo videos to better showcase what the product is all about.
Add structure to your content whenever possible.
Create content for all stages of the funnel. That means creating content for different kinds of users who are at different stages of buying.
Bottom Line
SEO for eCommerce stores is an ongoing process. But, make sure to take care of all the things mentioned in this post to see surefire improvement.
Author
Mike is an SEO expert and digital marketing consultant who helps small and mid-size businesses generate more leads, sales and grow revenue online. He offers expert advice on marketing your company the right way through performance-based SEO digital marketing, web design, social media, search engine marketing and many other online practices.




